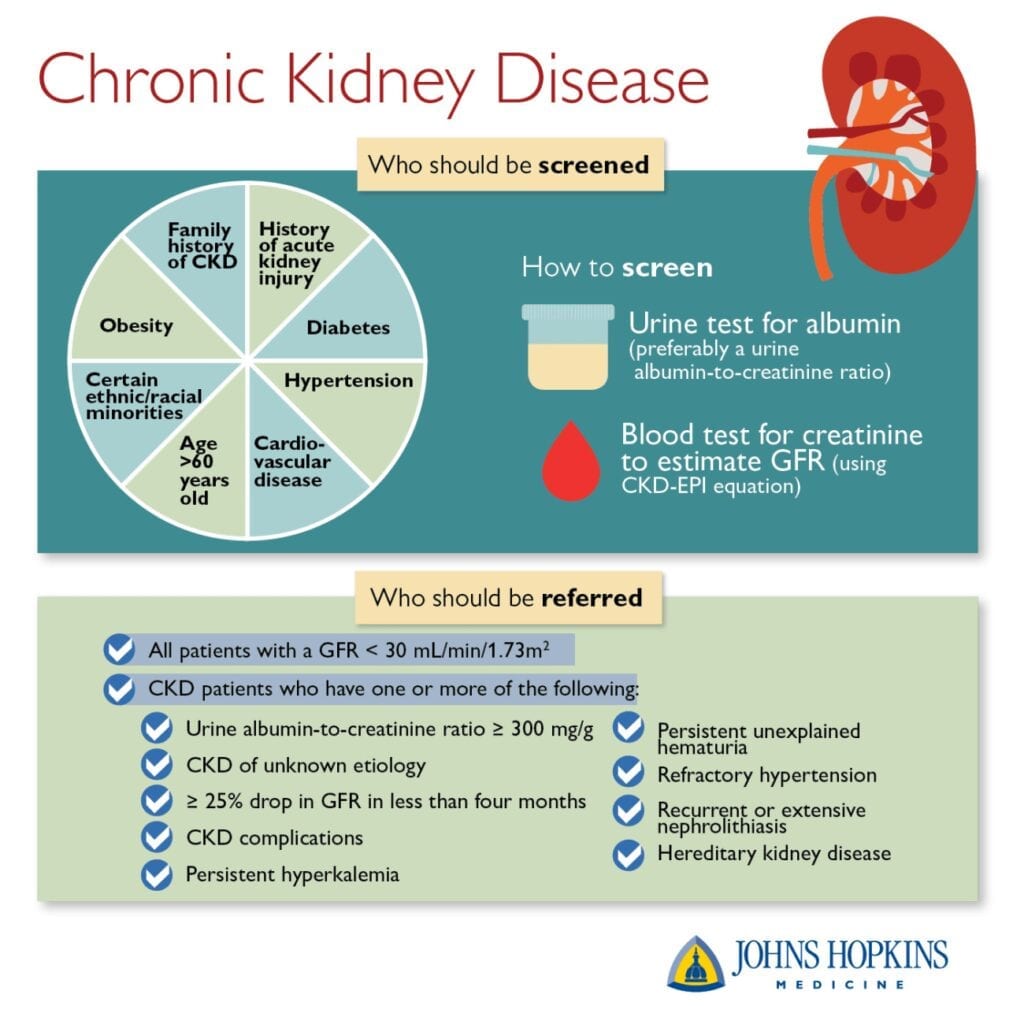
According to the CDC, over 37 million people in the U.S. are estimated to have Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Up to 50% of those with low kidney function may not even know that they have CKD. The kidneys are very complex and the process of diagnosing CKD can be very frustrating. Here is a brief overview of CKD and its symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
Symptoms
There are a wide variety of different symptoms for CKD. For many, symptoms may not even be present until there is already significant kidney damage. If several of these symptoms are observed, it is highly recommended to speak to a primary care physician about getting tests done to check kidney function. These symptoms include:
· Swelling around eyes or legs
· Fatigue, drowsiness, insomnia, sleep apnea
· Shortness of breath, urine-like odor in breath
· Nausea, vomiting, blood in stool, weight loss
· Excessive thirst, hiccups
· Muscle twitching or cramping, bruising or bleeding easily, bone pain
· Numbness in hands and feet
· Decreased interest in sex and impotence
Treatment
There are 5 different stages of CKD that one can be diagnosed with. When diagnosed with stages 1-4, the damage that has already been done cannot be reversed, but treatment will help slow down the progression of the disease. The first step is to identify if there is an underlying disease present that needs to be addressed and treated. Simultaneously, the kidney specialty team will discuss other lifestyle changes and interventions that are appropriate, which may include:
· Reducing fat, sodium, protein, and potassium intake
· Exercising daily
· Quitting smoking
· Taking supplements/medication to help with symptoms and electrolyte imbalances such as: vitamin D, calcium, stool softeners, phosphate binders, antihistamines, and erythropoietin injections.
For many diagnosed with CKD, the disease does progress to stage 5 or end-stage renal disease (ERSD). This stage is determined by kidney function being less than or equal to ten percent. Once this is determined, dialysis or a transplant is necessary.
Dialysis is a process in which waste is removed from the blood and electrolytes are balanced. There are two different types: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis is done in a dialysis center, and peritoneal dialysis can be done remotely. Dialysis is a lengthy process and may need to be done for several hours, multiple times a week. Dialysis is a very invasive process and requires a lot of lifestyle changes.
Prevention
Although CKD and ERSD cannot necessarily be prevented, it is imperative to prevent the underlying disease from worsening and leading to CKD. The top two conditions that lead to CKD are diabetes and hypertension. In order to prevent these conditions from getting worse, staying compliant with one’s medication, getting regular exercise and eating a low-carb and low-sodium diet is necessary. For more detailed information about CKD and dialysis, please visit the National Kidney Foundation. If you or your loved one has recently been diagnosed with CKD and would like to start a plan for long-term care, WellPath Partners is here to help and provide any resources that you may need.
WellPath Partners is your senior resource referral guide. Follow us on ALL social media platforms and join us weekly for more content and public health discussions.
By: Leila Lagandaon
Placement Coordinator at WellPath Partners
B.S. in Health Science, California State University, Long Beach
